The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the four major ligaments in the knee joint. It is crucial in providing stability and preventing excessive forward movement of the tibia (shinbone) relative to the femur (thighbone). ACL health and injuries are common, especially in sports involving sudden stops, direction changes, or jumping.
Understanding the basics of ACL health and injury can help individuals recognize the importance of prevention and seek appropriate treatment. At Paris Orthopedics, we aim to give you the information you need to stay healthy and avoid injury.
Basics of ACL Health and Injury
What Is The ACL?
The ACL is a strong band of connective tissue deep within the knee joint. It connects the femur to the tibia and works with other ligaments, muscles, and tendons to maintain stability during various movements. The ligament consists of two bundles that work together to control the rotational and forward movement of the knee.
How Do ACL Injuries Occur?
ACL injuries typically occur due to sudden, forceful movements or impacts that place excessive stress on the ligament. Common mechanisms of injury include sudden stops or pivots, abrupt changes in direction, landing awkwardly from a jump, or direct blows to the knee. Female athletes, especially those participating in sports like soccer, basketball, and gymnastics, have a higher risk of ACL injury than males.
When an ACL injury occurs, individuals may experience a popping sound or sensation in the knee, followed by immediate pain, swelling, and instability. The knee may feel weak and give way during movement, making it difficult to bear weight or participate in physical activities. In some cases, associated injuries, such as damage to the meniscus or other ligaments, may also occur.
What Does Treatment Look Like?
Diagnosing an ACL injury involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. The healthcare provider will assess the knee joint’s range of motion, stability, and overall function. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to evaluate the extent of the injury and rule out other knee conditions.
Treatment options for ACL injuries depend on various factors, including the severity of the injury, the individual’s activity level, and the presence of associated injuries. Non-surgical treatment may suit individuals with partial tears or those without high-demand activities. It typically involves physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, bracing to provide stability, and activity modification.
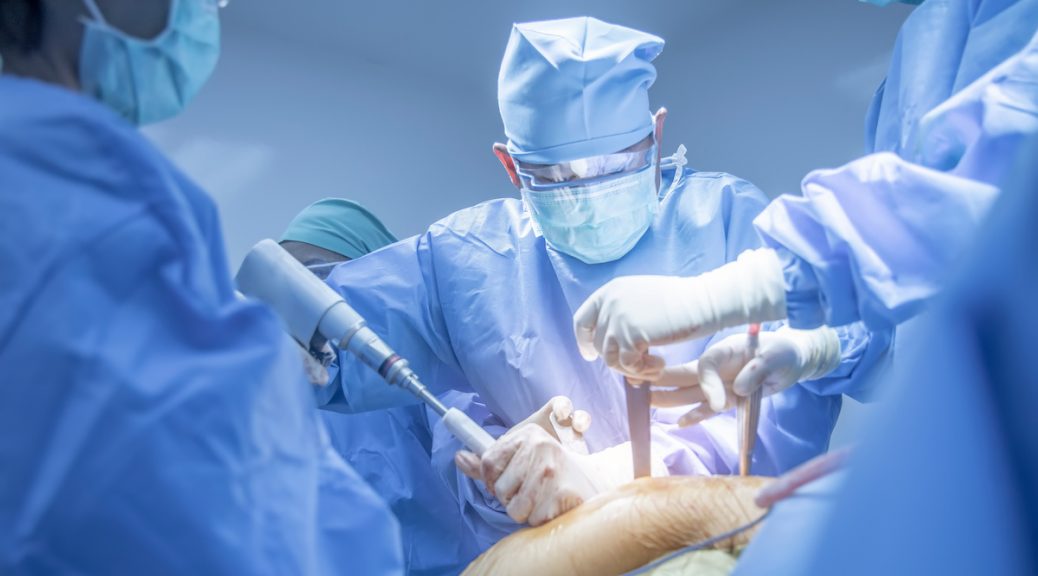
Surgical intervention may be recommended for individuals with complete tears or those wanting to return to high-demand sports or activities. ACL reconstruction surgery involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, typically harvested from the individual’s hamstring or patellar tendon, or using donor tissue. The surgery aims to restore knee stability and allow individuals to return to their pre-injury level of activity with proper rehabilitation.
What Does Recovery Look Like?
Recovery from an ACL injury requires a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Physical therapy is vital in restoring strength, range of motion, and stability to the knee joint. The rehabilitation process typically includes exercises to improve flexibility, balance, proprioception, and gradual return to sports-specific activities.
How Can You Prevent These Injuries?
Preventing ACL injuries is crucial, particularly for individuals engaged in high-risk sports. Strategies for prevention include regular conditioning and strengthening exercises to improve lower limb strength and control, proper technique training for jumping and landing, and wearing appropriate protective gear. Additionally, maintaining good overall physical fitness, warming up adequately before activities, and avoiding overuse and fatigue can help reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
Learn More With Paris Orthopedics
The ACL is a critical ligament in the knee joint, providing stability and preventing excessive forward movement. ACL injuries are common, particularly in sports involving sudden stops, changes in direction, or jumping. Understanding the basics of ACL health and injury empowers individuals to recognize the signs, seek appropriate treatment, and take preventive measures.
Are you interested in learning more about ACL health? Our team at Paris Orthopedics has an array of resources and information for you to use. Find out more by visiting our website or giving us a call at (903) 737-0000.