Joint pain can significantly impact your daily life, making simple activities like climbing stairs or opening jars feel like major challenges. At Paris Orthopedics, we regularly help patients understand and address their joint pain. Here’s what you need to know about common causes of joint pain and when to seek professional medical attention.
Understanding Joint Pain
Joint pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. It may affect any joint in your body, including knees, hips, shoulders, elbows, and fingers. While some joint pain is temporary and can be managed at home, other types require professional medical intervention.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
Osteoarthritis
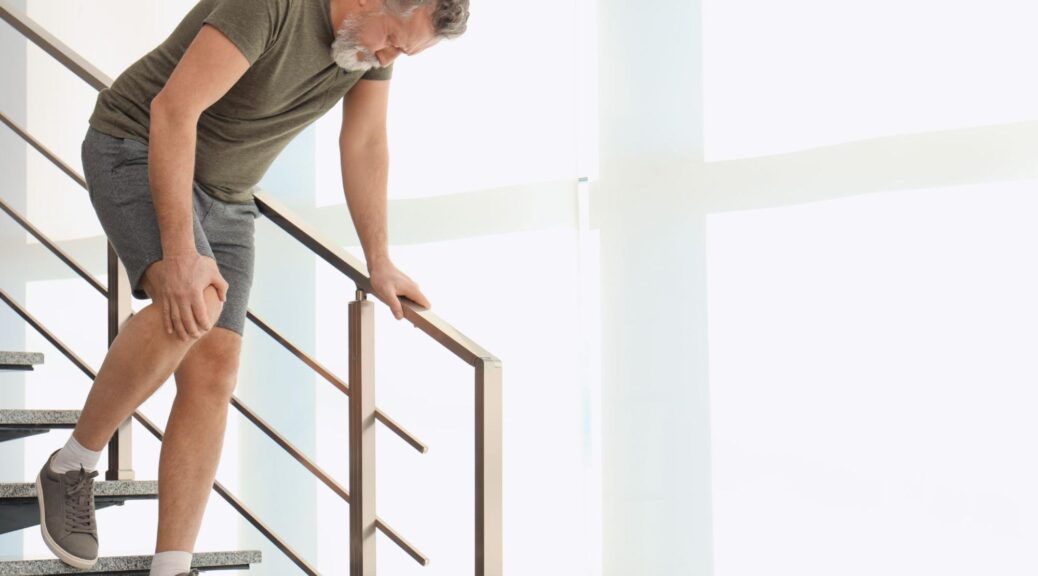
Osteoarthritis is the leading type of arthritis among adults. In this condition, years of joint use cause the smooth, protective cartilage between bones to break down and deteriorate gradually. As this cushioning layer diminishes, bones can begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This condition most commonly affects weight-bearing joints like knees and hips. Age, previous injuries, and excess weight can all contribute to its development.
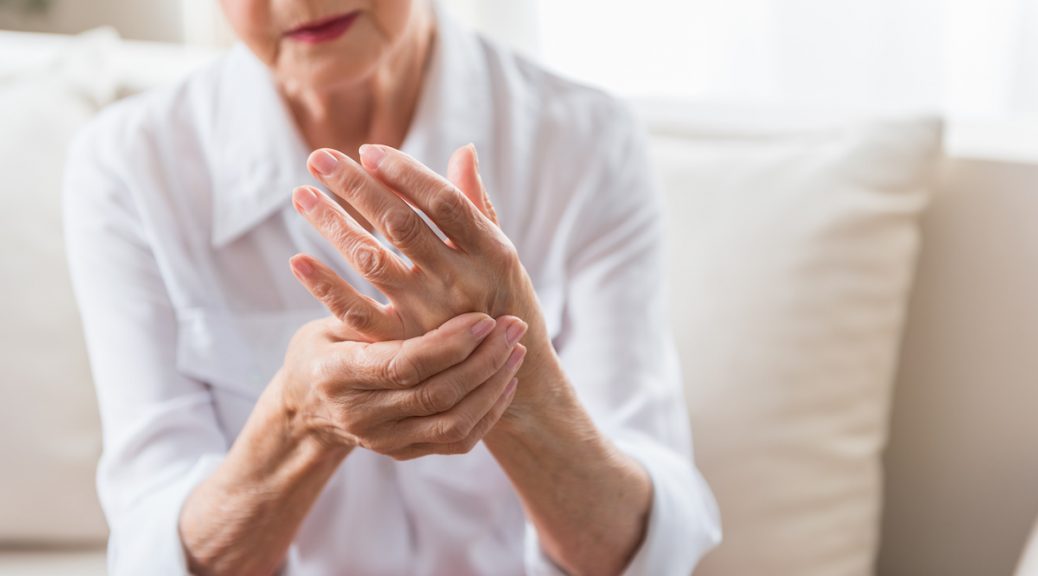
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where your immune system attacks the lining of your joints. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and eventual joint deformity if left untreated. RA typically affects multiple joints symmetrically (both sides of the body) and often starts in smaller joints like those in your hands and feet.
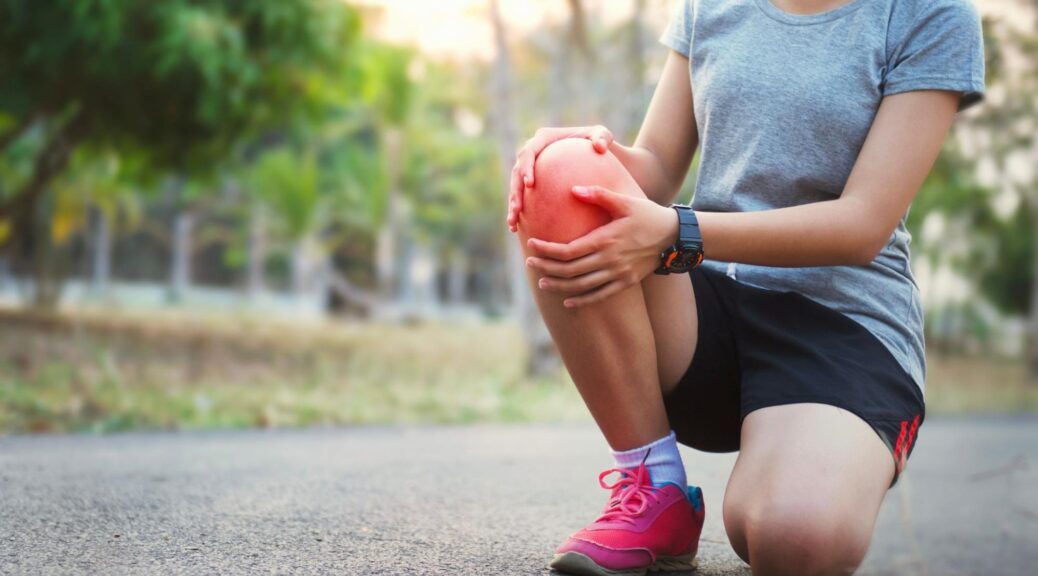
Sports Injuries
Active individuals frequently experience joint pain due to:
- Sprains and strains
- Tendinitis
- Bursitis
- Ligament tears
- Meniscus injuries
These injuries often occur during sports activities or exercise but can also result from everyday movements and overuse.
Gout
This form of arthritis occurs when uric acid crystals build up in joints, causing intense pain and inflammation. While gout most commonly affects the big toe, it can occur in any joint. Diet, genetics, and certain medical conditions can increase your risk of developing gout.
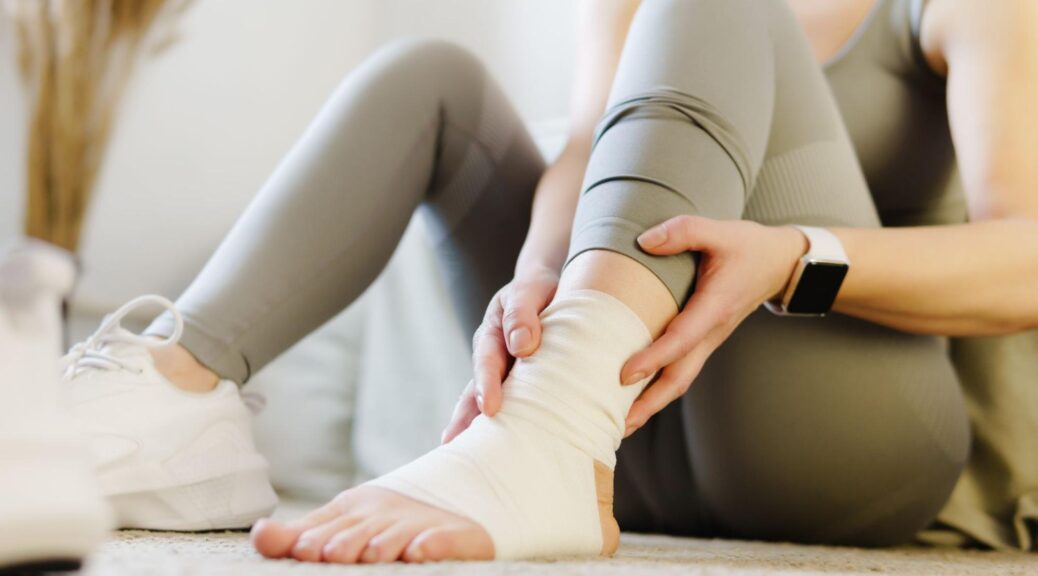
Overuse and Repetitive Motion
Many people develop joint pain from repetitive movements at work or during recreational activities. This can lead to conditions like:
- Tennis elbow
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Runner’s knee
- Shoulder impingement
When to Seek Treatment
While some joint pain can be managed at home with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers, certain symptoms warrant professional medical attention. Contact Paris Orthopedics if you experience:
Severe Pain or Swelling
Seek immediate care if your joint pain is severe or accompanied by significant swelling, especially if there’s no obvious cause for the symptoms.
Limited Range of Motion
If you’re unable to fully move your joint or if movement is significantly restricted, it’s time to see a specialist. This could indicate a serious underlying condition requiring prompt treatment.
Pain Lasting More Than Three Days
While minor aches might resolve on their own, persistent joint pain lasting more than three days should be evaluated by a medical professional.
Signs of Infection
Seek immediate medical attention if your joint is:
- Red and warm to the touch
- Accompanied by fever
- Extremely tender
These could be signs of a joint infection, which requires urgent treatment.
Impact on Daily Activities
When joint pain interferes with your normal daily activities or sleep, it’s time to seek professional help. Don’t let joint pain diminish your quality of life.
Treatment Options at Paris Orthopedics
Our experienced team offers various treatment approaches tailored to your specific condition:
Conservative Treatments
- Physical therapy
- Medications for pain and inflammation
- Joint injections
- Bracing or supportive devices
- Weight management guidance
- Exercise recommendations
Advanced Treatments
For more severe cases, we may recommend:
- Minimally invasive procedures
- Arthroscopic surgery
- Joint replacement surgery
- Regenerative medicine options
Prevention Strategies
While not all joint pain is preventable, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly with proper form
- Avoiding overuse and repetitive stress
- Using proper ergonomics at work
- Staying active but allowing adequate rest between activities
- Following a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet
Schedule a Consultation
Don’t let joint pain control your life. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe joint pain, schedule a consultation with Paris Orthopedics. Our specialized team will evaluate your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan to help you return to the activities you love.
Contact us today at 903-737-0000 to schedule an appointment. We serve patients throughout the Paris area with comprehensive orthopedic care focused on improving mobility and quality of life.
Remember: Early intervention often leads to better outcomes. Don’t wait until joint pain severely impacts your daily life before seeking professional help.